Introduction
In today’s digital landscape, user experience (UX) is a crucial factor in determining the success of any online presence. As we move into 2024, the importance of UX continues to grow, influencing customer satisfaction, engagement, and ultimately, business success. This blog delves into the significance of UX, the elements that contribute to a great user experience, and strategies to enhance it.
Understanding User Experience
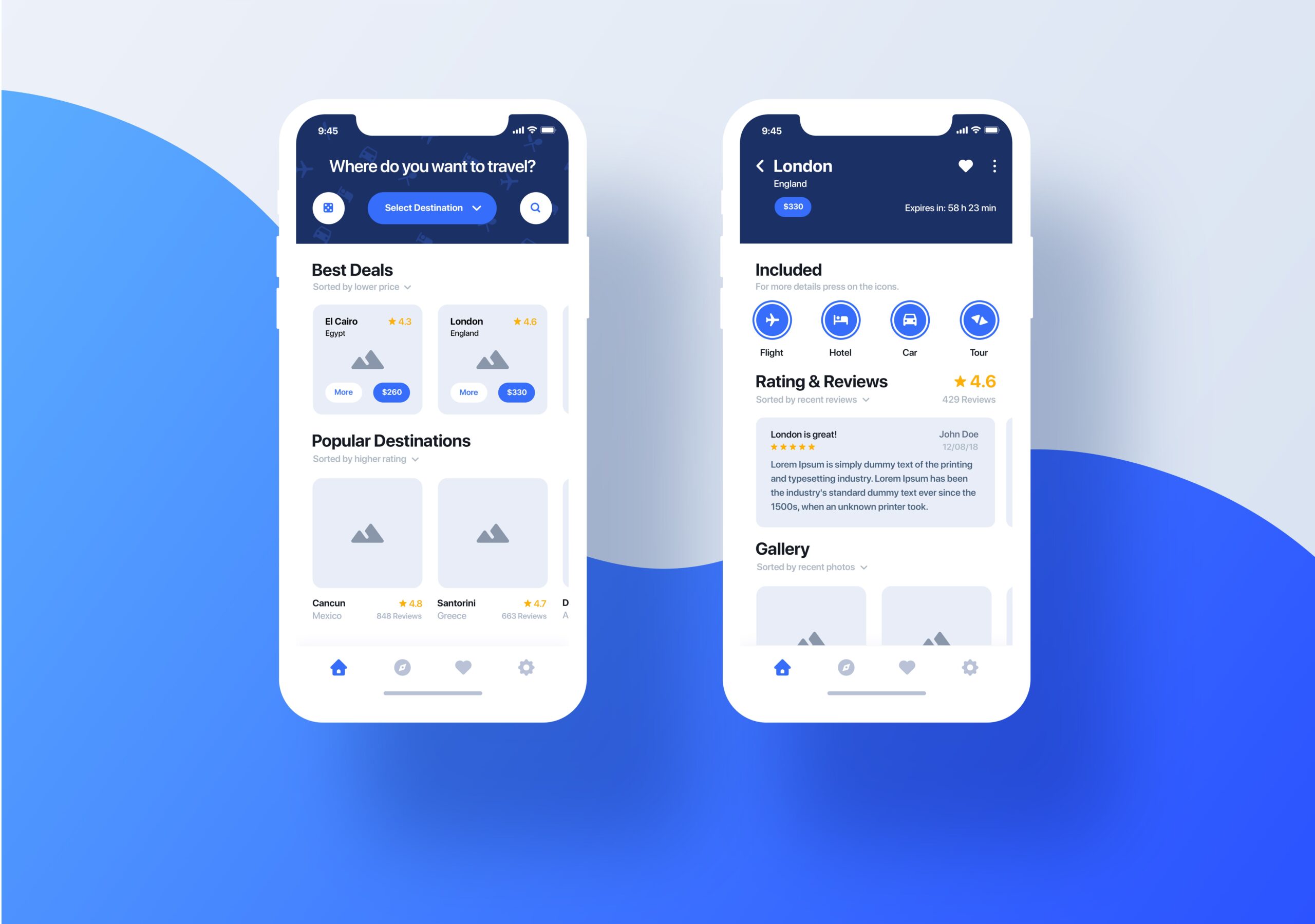
User experience encompasses all aspects of a user’s interaction with a product, service, or website. It includes everything from usability and accessibility to visual design and interaction. While often confused with user interface (UI), UX is a broader concept that focuses on the overall feel of the experience, whereas UI pertains to the specific design elements that users interact with.
A comprehensive understanding of UX requires recognizing its multidisciplinary nature. It draws from fields like psychology, design, and computer science to create an intuitive and efficient experience for users. UX professionals often employ various methodologies to ensure that the final product meets users’ needs and expectations. For a deeper dive into the principles of UX, consider exploring resources like Nielsen Norman Group’s UX Design Fundamentals.
The Impact of UX on Business Success
A well-designed UX can significantly boost customer satisfaction and loyalty. By providing a seamless and enjoyable experience, businesses can encourage repeat visits and positive word-of-mouth. Moreover, an optimized UX can lead to higher conversion rates and increased revenue, as users are more likely to complete desired actions when their journey is intuitive and pleasant.
Studies have shown that companies that prioritize UX see a substantial return on investment. According to Forrester Research, every dollar invested in UX brings $100 in return. This underscores the critical role that UX plays in not only retaining customers but also in driving profitability. For more insights into the business impact of UX, the User Testing blog offers detailed analyses and case studies.
Key Elements of a Great User Experience
- Usability: Ensures that users can achieve their goals efficiently. Usability is about making interfaces easy to navigate and ensuring that users can accomplish their tasks without frustration. This involves creating clear, straightforward interfaces and eliminating any unnecessary complexity.
- Accessibility: Makes the product usable by people of all abilities and disabilities. Accessibility is a legal requirement in many countries and an ethical imperative for all digital creators. It involves designing products that everyone, including people with disabilities, can use. Tools like WAVE can help evaluate and improve the accessibility of your website.
- Information Architecture: Organizes and structures content in a logical way. Good information architecture ensures that users can find what they’re looking for quickly and easily. It involves categorizing and structuring content in a way that makes sense to users. For more on information architecture, check out UX Design Institute’s guide.
- Interaction Design: Focuses on creating engaging interfaces with well-thought-out behaviors. Interaction design is about creating interfaces that are not only functional but also enjoyable to use. This involves considering how users interact with your product and designing interactions that are intuitive and satisfying.
- Visual Design: Uses aesthetics to improve user engagement and satisfaction. Visual design is about more than just making a product look good; it’s about using visual elements to enhance usability and user experience. This includes everything from the layout and color scheme to typography and imagery. For more insights on visual design, visit Smashing Magazine’s visual design section.
Strategies to Improve User Experience
- User Research and Personas: Understanding your audience through research helps tailor the experience to their needs. User research involves gathering insights about your users’ needs, behaviors, and motivations through various methods such as surveys, interviews, and usability testing. Creating personas helps in designing for different user types and ensuring that the product meets the needs of its target audience.
- User Testing and Feedback: Continuous testing and feedback loops ensure that the UX evolves with user expectations. User testing involves observing users as they interact with your product to identify usability issues and areas for improvement. Collecting feedback helps in understanding how users perceive your product and what changes are needed to enhance their experience.
- Implementing Responsive Design: Ensures that the website or application functions well on all devices. Responsive design involves creating web pages that look good and function well on a variety of devices and screen sizes. This is essential for providing a seamless experience to users, whether they’re on a desktop, tablet, or smartphone. For best practices in responsive design, refer to Google’s guide on responsive web design.
- Simplifying Navigation: Clear and intuitive navigation helps users find what they need quickly. Simplifying navigation involves designing menus and navigation structures that are easy to understand and use. This can significantly reduce frustration and improve the overall user experience. For tips on creating effective navigation, see Interaction Design Foundation’s article.
- Enhancing Loading Speed: Fast load times are critical for maintaining user interest and reducing bounce rates. Enhancing loading speed involves optimizing images, leveraging browser caching, and minimizing code. Tools like Google PageSpeed Insights can help identify and fix performance issues that affect your site’s loading speed.
Tools and Techniques for UX Optimization
Several tools and techniques can aid in optimizing UX. Popular UX tools like Figma, Sketch, and Adobe XD facilitate design and prototyping. A/B testing allows for comparing different versions of a design to see which performs better. Heatmaps and analytics provide insights into user behavior, highlighting areas for improvement.
- Figma: A cloud-based design tool that allows for real-time collaboration and prototyping. It offers robust features for wireframing, design, and prototyping, making it a popular choice among UX designers.
- Sketch: A vector graphics editor with a focus on UI and UX design. Sketch is known for its simplicity and efficiency, allowing designers to create high-fidelity designs and prototypes quickly.
- Adobe XD: An all-in-one UX/UI solution for designing websites, mobile apps, and more. Adobe XD offers powerful tools for designing, prototyping, and sharing user experiences.
- A/B Testing: A method of comparing two versions of a web page or app to see which one performs better. This involves testing different design elements, such as headlines, images, or call-to-action buttons, to determine which version leads to higher engagement or conversion rates. For a comprehensive guide to A/B testing, check out Optimizely’s A/B Testing Guide.
- Heatmaps and Analytics: Tools like Crazy Egg or Hotjar provide visual representations of user behavior on your site. Heatmaps show where users click, scroll, and spend the most time, offering valuable insights into how users interact with your site and where improvements can be made.
Case Studies of Successful UX Implementation
Examining real-world examples can provide valuable insights into effective UX strategies. Leading companies often set benchmarks with their innovative approaches, offering lessons and best practices that others can emulate.
- Spotify: Known for its seamless and intuitive user experience, Spotify constantly iterates on its design to meet user needs. By focusing on personalization and ease of use, Spotify has managed to create a highly engaging and enjoyable user experience.
- Airbnb: Airbnb’s success can be attributed to its user-centric design approach. The platform makes it easy for users to find and book accommodations, with a clean and intuitive interface that guides users through the process. Their focus on high-quality visuals and user-generated content adds to the overall experience.
- Amazon: Amazon’s UX design focuses on convenience and efficiency. Features like one-click purchasing, personalized recommendations, and a robust search function make shopping on Amazon easy and enjoyable. Their continuous optimization efforts ensure that the user experience remains top-notch.
Future Trends in User Experience
Looking ahead, several trends are set to shape the future of UX:
- AI and Machine Learning in UX: These technologies can personalize and enhance user experiences in real-time. AI can analyze user behavior and preferences to deliver personalized content and recommendations, while machine learning can optimize user interactions by predicting and adapting to user needs.
- Personalization and Adaptive Design: Tailoring experiences to individual users will become increasingly important. Adaptive design involves creating interfaces that automatically adjust to different user contexts and preferences, providing a more personalized and relevant experience.
- Voice User Interfaces: As voice technology advances, designing for voice interactions will be a key area of focus. Voice user interfaces (VUIs) offer a hands-free, intuitive way to interact with digital products, making them ideal for tasks like searching for information, setting reminders, and controlling smart devices. For more on the future of voice interactions, explore UX Design’s article on VUI.
Conclusion
In conclusion, user experience remains a vital aspect of digital strategy. Businesses that prioritize UX can expect to see improvements in customer satisfaction, engagement, and overall success. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, staying ahead of UX trends and continually optimizing the user experience will be essential.
Investing in UX is not just about creating beautiful interfaces; it’s about understanding your users, anticipating their needs, and delivering solutions that exceed their expectations. By focusing on usability, accessibility, and user-centered design, businesses can build products that not only attract users